Our Services
-
![]()
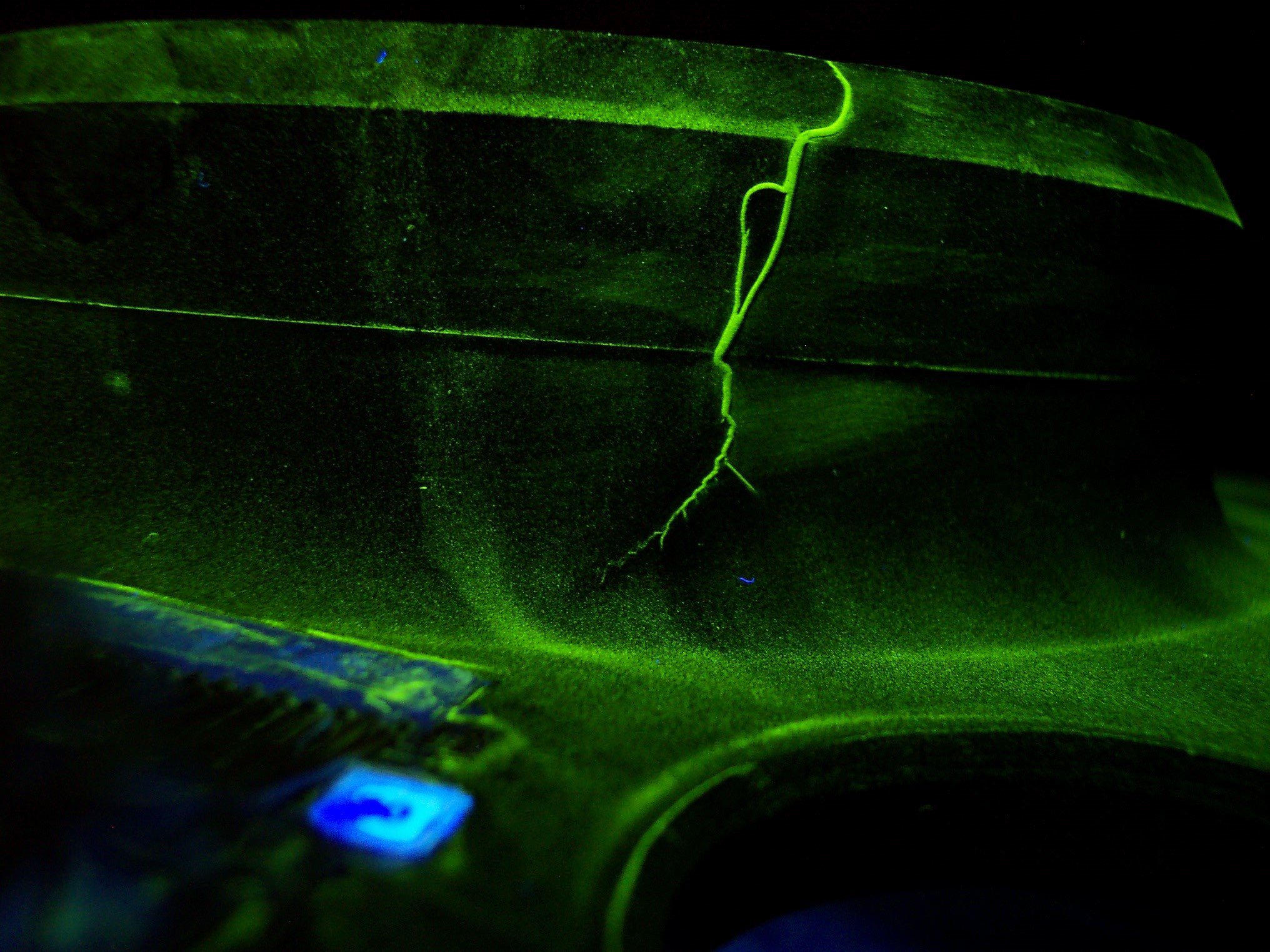
Fluorescent Penetrant Inspection
Fluorescent Penetrant Inspection is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing for the detection of discontinuities such as cracks, seams, laps, inclusions, cold shuts, laminations, shrinkage, porosity, and other surface defects in various materials like metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. It is widely used for the inspection of non-magnetic materials such as Aluminum, Titanium, Stainless Steel and Magnesium. It is a cost-effective and efficient method for quality control, ensuring the reliability and safety of materials and components without causing damage to the inspected parts.
-
![]()
Magnetic Particle Inspection
Magnetic Particle Inspection is commonly used in various industries to assess the integrity of critical components consisting of weldments, castings, forgings and other wrought materials. It is a versatile and widely accepted method for identifying defects on the surface or slightly below the surface in ferromagnetic materials without causing damage to the tested components.
-
![]()
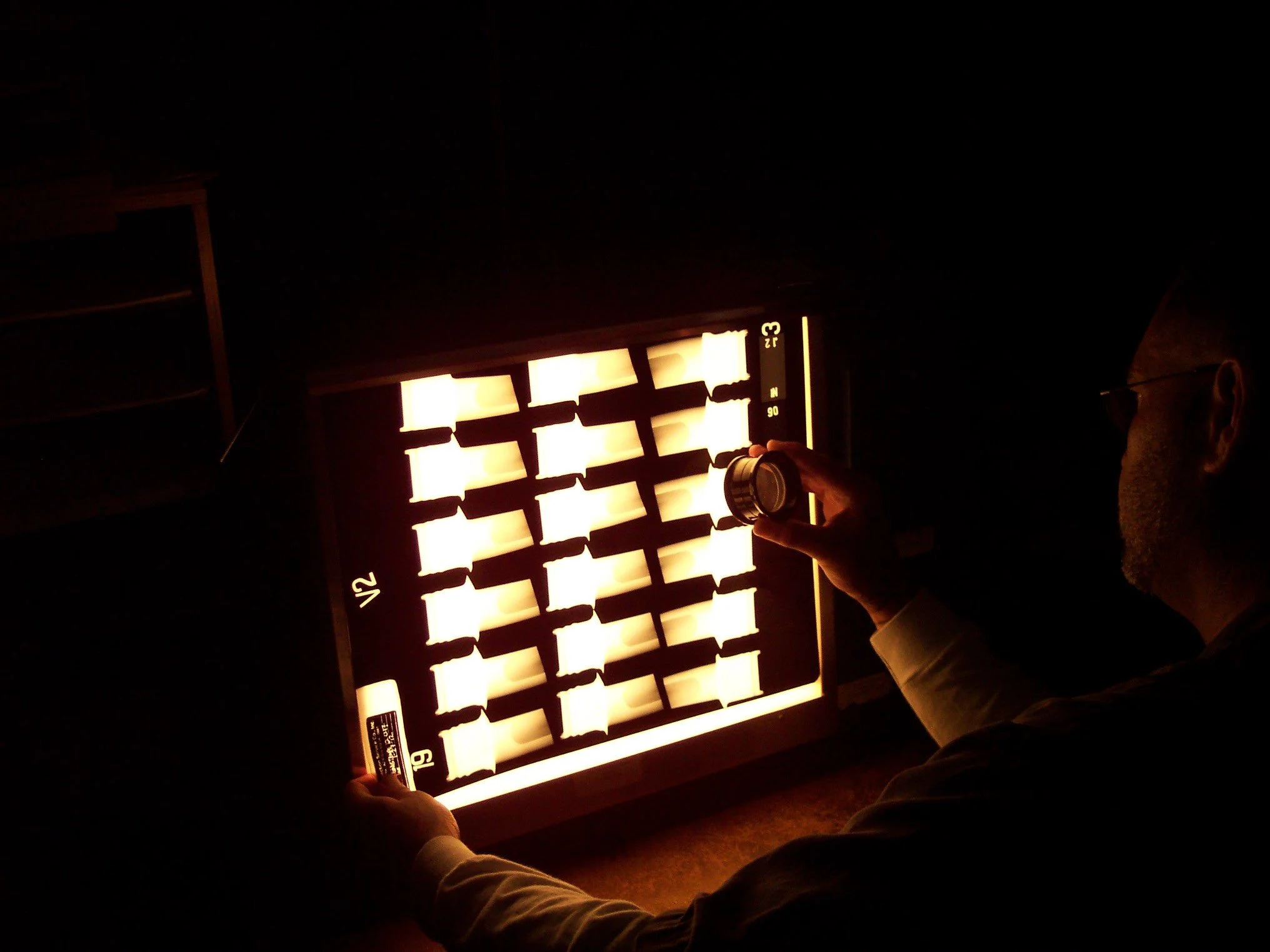
Radiographic (X-Ray) Inspection
Radiographic (X-Ray) Inspection is widely employed in industries such as aerospace, and manufacturing, where the internal integrity of materials needs to be assessed without causing damage to the components.
-
![]()
Passivation
Passivation is a chemical process used to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. The objective is to create a protective oxide layer on the metal's surface, which helps prevent corrosion and improve the material's longevity. Passivation is commonly used in various industries, including aerospace, electronics, and automotive.
Passivation provides several benefits, including improved corrosion resistance, enhanced cleanliness, and increased durability of metal components. It is a critical step in the manufacturing and maintenance of stainless steel and other corrosion-resistant alloys used in various industries.
-
![]()
General & Pre-Weld Clean
Cleaning is the removal of contaminants such as dirt, grease, oil, rust, and other foreign materials from the metal surface. This can be achieved through various methods, including solvent cleaning, alkaline cleaning, acid cleaning, or mechanical methods.
Once contaminants are removed, the metal surface may need further preparation, depending on the specific application.
Proper cleaning procedures contribute to the overall quality, strength, and durability of machined parts and welded joints. They also play a significant role in preventing defects and ensuring the long-term performance of metal components.
-
![]()
Abrasive Blasting
Abrasive blasting, also known as glass bead blasting, is a surface preparation technique used to clean or abrade a material's surface by propelling abrasive media against it at high velocity. This process is commonly employed in various industries for tasks such as removing paint, rust, scale, or other contaminants, as well as preparing surfaces for coatings or bonding.
Abrasive blasting is a versatile and widely utilized method for surface preparation, offering efficiency and effectiveness in various industrial applications.